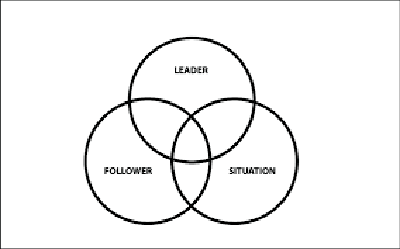
Interactional approaches to leadership represent an advanced development of situational leadership theories within the broader field of leadership theories and research. These approaches aim to refine the understanding of effective leadership by analyzing how various situational variables interact with one another over time.
The core idea of interactional leadership models is that leadership effectiveness is not solely determined by the traits of the leader or by static situational conditions—but by the dynamic interplay between:
-
The personality of the leader and the followers,
-
The structure and dynamics of the group,
-
And the specific characteristics of the task or work environment.
In this view, situational variables are not fixed. Instead, they are seen as mutually influential and evolving: leaders influence the situation, and the situation, in turn, influences leaders and followers. This reciprocal influence introduces a level of complexity that makes it challenging to formulate a single, unified interactional leadership theory.
Nonetheless, interactional approaches have been instrumental in highlighting the complex, relational nature of leadership and reinforcing the idea that leadership cannot be reduced to a set of universal traits or one-size-fits-all strategies. While these models may not produce rigid predictive frameworks, they offer valuable insights for adaptive leadership in real-world, evolving environments.
« Back to Glossary Index