Also known as: Work motivation, employee motivation
Motivation refers to the internal and external drivers that influence a person’s decision to act in a certain way—particularly in the workplace. In the context of human resource management and organizational behavior, motivation plays a central role in determining employee performance, commitment, and job satisfaction.
Definition and Components of Work Motivation
According to Becker, work motivation arises when an employee perceives incentives or stimuli in their work environment that activate individual motives in such a way that they trigger or influence performance behavior (→ performance behavior). It is best understood as the interaction between a motivated individual and a motivating work environment.
Work motivation is often divided into two key dimensions:
-
Participation (or Retention) Motivation
The desire or willingness of an individual to join, remain in, and engage with an organization or specific work role. -
Achievement Motivation
The internal or external conditions that drive a person to perform beyond basic expectations, often linked to personal goals, pride in work, or ambition.
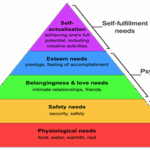
Olfert broadens the definition, describing motivation as all the internal and environmental factors that prompt individuals to behave in specific ways. Depending on the context, this includes work motivation and learning motivation.
Types of Motivation
Motivation can be intrinsic or extrinsic, each with distinct influences on employee behavior:
-
Internal (Intrinsic) Motivation
Originates from within the individual, driven by personal motives such as:-
Achievement and competence
-
Curiosity and learning
-
Personal growth and autonomy
-
Financial goals (e.g., wealth-building)
This form of motivation tends to be longer-lasting and more self-sustaining, often linked to personal attitudes, willpower, and goal-setting.
-
-
External (Extrinsic) Motivation
Triggered by external incentives provided by managers or the organization, such as:-
Praise or recognition
-
Salary, bonuses, or benefits
-
Promotion opportunities
-
Social status and team belonging
-
Professional development
These are common leadership tools that managers use to influence and reinforce performance behavior.
-
Motivation and Leadership
Motivation is deeply interconnected with leadership. Managers influence employee motivation by:
-
Setting clear goals
-
Offering constructive feedback
-
Using performance appraisals and incentive systems
-
Providing development opportunities
Motivation is also affected by social influences within teams, peer groups, and the broader organizational culture.
« Back to Glossary Index




![15 Employee Offboarding Templates That Save Hours of HR Time [Free Downloads] 15 Employee Offboarding Templates That Save Hours of HR Time [Free Downloads]](https://i1.wp.com/www.hrcloud.com/hubfs/Header.png?w=150&resize=150,100&ssl=1)
