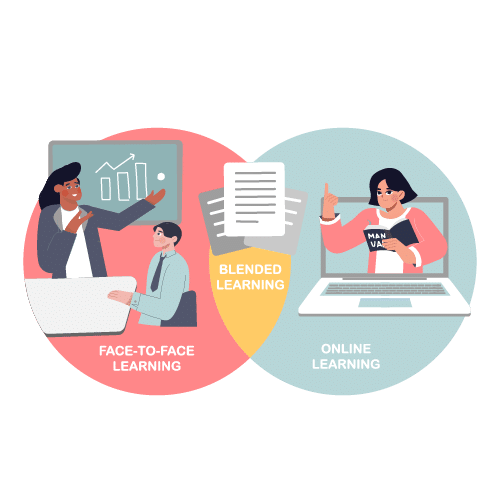
Blended learning is an integrated learning concept that combines the use of information and communication technology (ICT), such as the internet, intranet, and/or telephone conferences, with traditional learning methods in a single learning arrangement.
While the term “blended learning” has become more frequently used in the continuing education environment in recent years, as emphasized by Hofmann and Regnet (2003), the concept itself is not new. Blended learning incorporates various methods, such as:
-
Workshops or seminars that incorporate telephone or video conferences (e.g., with experts who cannot attend in person).
-
Continuing education courses that include ongoing communication via email between participants and instructors during non-event periods.
Key Benefits of Blended Learning
According to Hofmann and Regnet (2003), blended learning offers several advantages:
-
Cost-effective bridging of geographical distances: The approach allows for expertise to be brought in from anywhere in the world, particularly beneficial for internationally composed groups. It also utilizes the time between seminar modules for continued learning, even when participants are geographically dispersed. The main limitation is the difference in time zones.
-
Wide variety of learning formats: Blended learning accommodates different learning styles, enabling participants to engage in formats that suit their individual preferences, whether through synchronous or asynchronous methods.




![15 Employee Offboarding Templates That Save Hours of HR Time [Free Downloads] 15 Employee Offboarding Templates That Save Hours of HR Time [Free Downloads]](https://i1.wp.com/www.hrcloud.com/hubfs/Header.png?w=150&resize=150,100&ssl=1)
